Wednesday, December 17, 2014
Tree in data structure What is tree ?
What is tree
Definition:- Tree is is hierarchical (or non-linear) data structure.
or
Tree is a finite set of elements that is either empty or partitioned into three disjoint subsets ,the first subset contains a single element called the root of the tree.The other two subset are themselves tree called left and right subtree of original tree .Each element of tree is called a node of the tree .
Important Term related with trees-
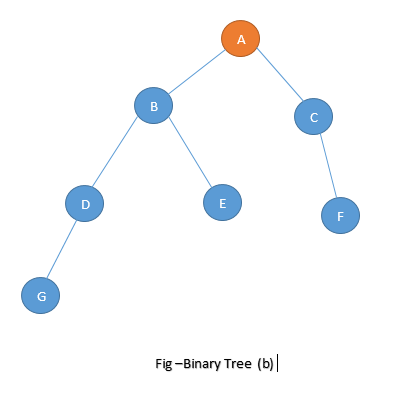
Root Node- The First Subset or single element called root or parent node of the tree (Such as A is the root node in above figure)
Leaf Node - The node that has no son is called leaf node of tree (Such as D,E,F,G are the leaf node in above fig)
Sibling- Two nodes are sibling if they have same parent (such as D,E and F,G are siblings)
Level of tree- The level of a node in binary tree is the number of edges traversed from the root node to the node i.e. root has 0 level and level of any other node is one more than the level of its parents (such as level of below tree is 3 )
Depth of Tree- The depth of tree is the maximum level of any leaf in the tree ( such as depth of below tree is 4)
Climbing- Going from the leaves to the root is called "climbing"
Descending - Going from the root to the leaves is called descending
Types of Tree in data structure -Binary Tree Lecture 2
Types of Binary Trees?What are the different type of Binary Tree?
Types of Binary Trees
1. Strictly Binary Tree-
- If Every non leaf node in binary tree has non empty left and right subtrees ,the tree term as strictly binary tree .
Important Point for Strictly Binary Tree-
- Every non-leaf node has degree 2
- A strictly binary tree with n leaves has (2n -1 ) nodes
- Thus strictly binary tree has odd number of nodes
2. Complete Binary Tree -
- A complete Binary tree of depth d is the strictly binary tree whose all leave are at level d
- A Complete Binary Tree of depth d is the binary tree that contains exactly 2^l (two ki power l nodes )
- Issi prakar kisi bhi complete Binary tree (CBT) mein total no of nodes (2^d+1 -1) where d is depth of tree
- Isse ek conclusion ye nikalta hai ki complete Binary Tree hamesha Strict Binary tree hogi but strict binary tree hamesha complete binary tree (CBT) nhi hogi
- Jaisa ki hum jante hai CBT Hamesha Strict Binary tree hogi tab agar iske n leaves honge to isme total no of nodes 2n-1 honge
Tuesday, December 16, 2014
What is Binary tree,Different type of tree in Data structure
Different type of tree in Data structure
Binary Tree:-
- A Binary tree is a finite set of elements that is either empty or is partitioned into three disjoint subset
- The First subset contains a single element called the root of the tree
- The other two subsets are themselves binary tree ,called left and right subtrees of the original tree.
- Each element of a binary tree called a node of the tree
Friday, December 5, 2014
MCQ of DBMS fundamental question
MCQ Data Base Management System on Basic Fundamental
Q1.A Specific example where physical data independence would not hold is
- When data file is changed from unordered file to sorted file
- When additional access structure (Example an index ) is created for relation
- When DBA decides to store the data in B+ tree
- When the user writes an application program to join tables
Q2.Integrity means________
- Protecting the data against unauthorized users
- Protecting data against authorized users
- Making sure users are allowed to do the thing they are trying to do
- None of These
Q3.Controlling redundancy in database management system help to
- Avoid duplication of effort
- Avoid unnecessary wastage of storage space
- Avoid Inconsistence among data
- All of the above
Q4. Which of the following function not performed by DBA?
- Planning ,designing ,and implementation of database system
- Allocation of storage locations and data structures
- Establishing standards and procedures system
- Communicating with data base users
Q5.Which of the following is not an advantages of database approach ?
- Elimination of the data redundancy
- Ability to associate related data
- increased security
- All of the above
Q.6 A data Dictionary doesn't provides information about
- Where data is located
- The size of the disk storage
- Who owns or responsible for the data
- How data is stored
Q7.The data base administrator is ,in effects ,the coordinator between the _____and the ____
- DBMS ; database
- Application program ; Database
- Database ;Users
- Application programs ;Users
Q.8 Which of the following is not usually part of the responsibilities of a DBA?
- Approving Structure changes to the database
- Designing data entry screens
- Ensuring that an adequate backup regime is in place
- Issuing Accounts to users and monitoring the performance of the system
- Physical keys ,but the relation model is faster because it uses logical keys.
- Logical keys ,